Table of Contents
Web service
apache
- start, stop http server
service httpd start service httpd stop
- http version
httpd -v => Server version: Apache/2.2.3 Server built: Jan 21 2009 22:01:41
webmin
Webmin is a web-based interface for system administration for Unix. Using any modern web browser, you can setup user accounts, Apache, DNS, file sharing and much more.
refer
http://doxfer.com/Webmin/Modules http://www.webmin.com/
install on linux
- pre setup(for https)
yum -y install perl perl-Net-SSLeay openssl perl-IO-Tty perl-Encode-Detect
- Download and install from rpm package:
wget http://prdownloads.sourceforge.net/webadmin/webmin-1.930-1.noarch.rpm rpm -U webmin-1.930-1.noarch.rpm
with webmin new version: we copy the webmin source to /usr/local before setup
- install from source
./setup.sh => install from source with default port: 10000
- uninstall it:
/etc/webmin/uninstall.sh
install on Windows
refer:
Below are steps to Install Webmin on Windows:
- Step1: Install activeperl 32bits(not 64bits) ⇒ Because webmin only support perl 32bits(version in example is ActivePerl-5.24.0.2400-MSWin32-x86-64int-300560)
- Step2: Download webmin zip file for windows from http://www.webmin.com/download.html and unzip it to c:\webmin(Version in document is http://prdownloads.sourceforge.net/webadmin/webmin-1.820.zip)
- Step3: Append c:\webmin in Environment Variable PATH change.
- Step4: Download http://retired.beyondlogic.org/solutions/processutil/process203.zip and copy it to c:\webmin
- Step5: Go to c:\webmin and Install the Win32::Daemon Perl module.
cd c:\webmin ppm install Win32-Daemon
- Step6: install webmin(You must run DOS as admin):
perl setup.pl
With configs below:
For config, type "c:\etc" For logs, type "c:\temp" type 10000 for port no ssl
- Step7: Go to http://localhost:10000 to login webmin and refresh modules
config file and start, stop webmin
- config file:
/etc/webmin/miniserv.conf
- start:
/etc/webmin/start
- stop:
/etc/webmin/stop
create webmin user and config
- Step1: Go to webmin admin site, Create webmin user in webmin/webmin users
- Step2: Edit new user and check in Available webmin modules some options below:
- hardware/System time
- custom commands
- Step3: Change permission of user to limit “not edit”:
- In section Available webmin modules select module custom commands and set limit
reset password admin of webmin
All users and pass of webmin store in /etc/webmin/miniserv.users
- Step1: Find file changepass.pl where to install webmin
- Step2: Change the script change pass:
./changepass.pl /etc/webmin/ admin admin@123
copy custom commands
- Step1: Copy custom commands from old host to new host
tar czpf custom.tar.gz custom/ scp custom.tar.gz root@10.30.31.131:/etc/webmin/ tar xf custom.tar.gz cp custom/* /et/web/custom1
- Step2: Login to admin and click link Refresh Modules to load new custom command
- Step3: Go to Webmin Configuration→Module Titles to change the name of custom command to new name
- Step4: re-login to see updates
phpmyadmin
phpMyAdmin is a free software tool written in PHP intended to handle the administration of MySQL over the World Wide Web
Refer
http://www.atomicorp.com/wiki/index.php/PHP
phpMyAdmin-3.2.0.1-english/Documentation.txt
Require
at least PHP 5.2 and MySQL 5
- Step 1) Set up the atomic channel:
- wget -q -O - http://www.atomicorp.com/installers/atomic.sh | sh
- Step 2) Upgrade to PHP 5.2.x: yum upgrade
- Step 3) Replace the PHP 4 php.ini with PHP 5.2.x's (if applicable):
- mv /etc/php.ini.rpmnew /etc/php.ini
- Step 4) Replace the php.conf with the PHP 5.2.x php.conf (if applicable):
- mv /etc/httpd/conf.d/php.conf.rpmnew /etc/httpd/conf.d/php.conf
- Step 5) Restart the webserver
service httpd restart (or) /etc/init.d/httpd restart
prepare code phpMyAdmin and check installed packages
- copy phpMyAdmin-3.2.0.1-english to /var/www/html
- check php, create phpinfo.php:
<?php phpinfo(); ?> check http://192.168.191.128/phpinfo.php
- check install packages for mysql:
yum list | grep mysql => mysql.i386 5.0.83-1.el5.art installed mysql-devel.i386 5.0.83-1.el5.art installed mysql-libs.i386 5.0.83-1.el5.art installed mysql-server.i386 5.0.83-1.el5.art installed php-mysql.i386 5.2.9-2.el5.art installed php-mcrypt.i386 5.2.9-2.el5.art installed
config auto start httpd and mysqld
chkconfig httpd on chkconfig mysqld on
access phpMyAdmin
check https://192.168.191.128/phpMyAdmin user permissions: root
=> you must click "change administration password" on webmin before login to phpMyAdmin
squid: Web proxy
- install:
- start:
- /usr/local/squid/sbin/squid -N -d 1 -D
- config:
- /usr/local/squid/etc/squid.conf
- error:
- error message:
/usr/local/squid/var/logs/cache.log: Permission denied cat /var/log/messages Sep 10 00:54:13 GWServer01-DT05 squid: Cannot open
- Fix: '/usr/local/squid/var/logs/access.log' for writing. The parent directory must be writeable by the user 'nobody', which is the cache_effective_user set default in squid.conf. ⇒ fix:
chown -R nobody.nobody /usr/local/squid/var user squid
ftp server vsftpd
start, stop ftp server
service vsftpd start service vsftpd stop chkconfig --level 345 vsftpd on chkconfig --list vsftpd
configuration file
/etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf /etc/vsftpd/ftpusers /etc/vsftpd/user_list
Login Permit/Deny
access list
- Normally users which have an account on the local system ⇒ can log in using their login credentials (username and password) and access their files. As a security measure, not all system accounts should be allowed to do this.
- Any user account that is listed in /etc/vsftpd.ftpuser ⇒ will not be granted login access through vsftpd at all. This file is normally used for system accounts like root, bin etc. and users we do not want to allow login via FTP. By the way, putting the user anonymous in /etc/vsftpd.ftpuser does nothing. Anonymous access must be disabled explicitly with anonymous_enable=NO as explained above.
- Black list:
userlist_deny=YES userlist_enable=YES userlist_file=/etc/vsftpd/user_list
⇒ any user listed in /etc/vsftpd/user_list is NOT allowed to log in via FTP
- whitelisting
userlist_deny=NO userlist_enable=YES userlist_file=/etc/vsftpd/user_list
⇒ any user listed in the file /etc/vsftpd/user_list is now allowed to log in via FTP
create user to login ftp
- ftp user:pwd ftp
- other users:
- (for rhel and centOS) http://gob-blogs.blogspot.com/2008/02/ftp-error-500-oops-cannot-change.html
share home directories via ftp
If you want to share home directories via ftp please run:
setsebool -P ftp_home_dir 1
iptables open ftp port
Open port 21 for FTP:
*filter :INPUT ACCEPT [396:30624] :FORWARD ACCEPT [0:0] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [216:23216] -A INPUT -p tcp -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT #eth0 INPUT here -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 2222 -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 9999 -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -s 118.70.109.139 -i eth0 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 21 -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -p udp -i eth0 --sport 53 -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 4324 -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 4325 -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -i eth0 -p icmp -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -i eth0 -j DROP #eth1 INPUT here -A INPUT -i eth1 -p icmp -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -i eth1 -j DROP COMMIT
And addition ftp will use a random higher port. To allow this you need to load the ip_conntrack_ftp module on boot. Uncomment and modify the IPTABLES_MODULES line in the /etc/sysconfig/iptables-config file to read:
IPTABLES_MODULES="ip_conntrack_ftp"
samba
install
yum install samba.i386
start, stop samba service
service smb start service smb stop
log file
/var/log/samba/smbd.log
user management
- add user samba
- smbpasswd [options] [username]
- smbpasswd -a anhvc(extra options when run by root or in local mode:-a add user)
- disable user samba
- smbpasswd -d anhvc
- enable user samba
- smbpasswd -e anhvc
change security bool to share home directories via samba
setsebool -P samba_enable_home_dirs on create /home/share
ssh
overview about steps to create key-pair and using
- step1: Create an RSA(or DSA) key-pair, they were called private key and public key
- step2: Config for client can use private key to access remote machine(server)
- client: copy private key to directory ~./ssh
- server: add content of public key to ~/.ssh/authorized_keys to allow client can use private key access server
Generate keys 2048 bits
cd /home/anhvc/.ssh ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 2048 ssh-keygen -t dsa -b 1024
⇒ output:
id_rsa(or id_dsa) => private key(secrect key => authenticate for user anhvc id_rsa.pub(or id_dsa.pub) => public key
In case error “Saving ssh key fails”, you remove old directory .ssh and run again the command generate keys
rm -rf ~/.ssh
create file authorized_keys if not exist
mkdir -p .ssh or ssh-keygen -t dsa -b 1024 chmod 700 ~/.ssh touch .ssh/authorized_keys chmod 644 .ssh/authorized_keys
Change permissions in ssh
Sometimes you may do something to mess up these permissions. Run the following to fix most permissions problems. You may have to do this on both the remote host and local host.
chmod 700 ~/.ssh chmod 600 ~/.ssh/id_rsa chmod 644 ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub chmod 644 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys chmod 644 ~/.ssh/known_hosts
using private key to access remote machine(server) with putty
convert id_dsa to id_dsa.ppk for putty
email system in linux
The structure of email system contain 3 components: MUA(Mail User Agent), MTA(Mail Transfer Agent) and MDA(Mail Delivery Agent)
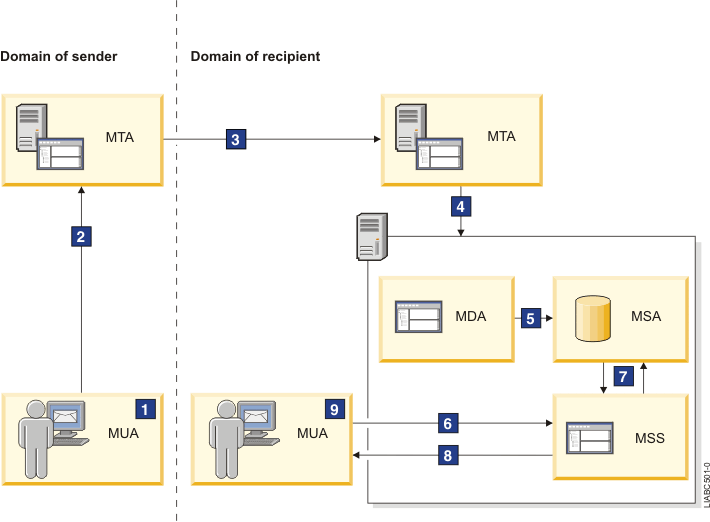
Figure: Basic Components of Email System
Email flows through the mail server components as follows:
- From their MUA, the sender creates an email and clicks Send.
- The MUA uses SMTP to send the email to an MTA.
- The MTA relays and routes the email to an MTA in the domain of the recipient.
- The MTA in the domain of the recipient sends the email to an MDA of the system of the recipient.
- From their MUA, the recipient reads the email created by the sender.
MUA (Mail User Agent)
An application with which users can create, view, send, and receive email. The MUA is located on a client system, such as a workstation or PC.
- Windows: Microsoft Outlook Express
- Linux: elm, pine, mutt,mail
mail -s “Hello world” [email protected] This is a test from my server Ctrl+D
MTA(Mail Transfer Agent)(mail router)
An application that sends, receives, and stores email. This program determines where and how to store email.
- Linux sendmail, postfix, qmail.
- Windows: Microsoft Exchange
MDA(Mail Delivery Agent)
An application that saves received email to the MSA. This program might also perform additional tasks such as filtering email or delivering email to subfolders.
The Postfix, Dovecot, and Cyrus applications each implement some or all of the functions of the MDA.
MSA(Mail Storage Area)
A local system or server where the MTA stores email. This is also the location from which the MSS retrieves email at the request of the MUA.
- Mbox
- Maildir
- /var/mail/spool/username/
MSS(Mail Storage Server)
An application that retrieves email from the MSA and returns it to the MUA.
- Dovecot
- Cyrus
NTP (Network Time Protocol)
Network Time Protocol(NTP) provides accurate and syncronised time across the Internet.
http://www.akadia.com/services/ntp_synchronize.html
we know that NTP clients can operate with NTP servers in three ways:
- in a client-server basis
- in a peer to peer mode
- sending the time using broadcast/multicast
architecture:
- NTP Server:10.30.31.127(Open UDP Port 123) for NTP protocol
- NTP Client: Windows 2000 or Unix(Linux, Solaris)
script:
- NTP server: 10.30.31.127
- date +%Y%m%d -s “20091125”
- NTP Client:
/usr/sbin/ntpdate -s -b -p 8 -u 10.30.31.127
Open Iptable firewall:
-A INPUT -i eth0 -p udp -m multiport --dports 123,161 -j ACCEPT
Or
-A INPUT -p udp -i eth0 --dport 123 -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -p udp -i eth0 --dport 161 -j ACCEPT
nfs
nfs server
check nfs server and Install It
- Check nfs server is running
ps -eaf | grep nfs
- Install Nfs Server
yum install nfs-utils nfs-utils-lib - Start Nfs server:
/etc/init.d/rpcbind start /etc/init.d/nfs start
config nfs server in /etc/exports
/work *(rw,no_root_squash,sync)
⇒ directory /work was exported and all host can use it
/databk/ztbackup/logzt 192.168.0.12(ro,no_root_squash) /databk/ztbackup/logzt 10.30.3.42(ro,no_root_squash) /databk/ztbackup/logzt 10.30.3.43(ro,no_root_squash) /databk/ztbackup/logzt 10.30.3.44(ro,no_root_squash) /databk/ztbackup/logzt 10.30.3.45(ro,no_root_squash) /databk/ztbackup/logzt 10.30.3.46(ro,no_root_squash)
⇒ directory /databk/ztbackup/logzt was exported and only hosts 192.168.0.12,10.30.3.42….46 can use it
/usr/sbin/exportfs -a /usr/sbin/exportfs
⇒ display configuration of nfsserver
active changes in /etc/exports
Linux:
/etc/init.d/nfs restart
debian:
/etc/init.d/nfs-kernel-server restart
create /work directory for nfsserver use
mkdir /work chmod 777 /work Copy rootfs from CD(2007WLP) to /work/rootfs-sgwp-080403-2-wtk.tar.bz2 and extract it.
nfs client with mount
Below are steps config in client with mount:
- Step1: Install nfs
yum install nfs-utils nfs-utils-lib - Step2: config mount in /etc/fstab:
10.30.31.8:/databk/ztbackup/db /data/dbzt nfs defaults 0 0 10.30.31.8:/databk/ztbackup/logzt /data/countitem/logzt nfs defaults 0 0 10.30.31.8:/databk/ztbackup/dbreport /var/lib/mysql nfs defaults 0 0
- Step3: active mount:
mount -a
Check nfs server with mount command:
- mount:
mount 10.30.31.8:/databk/ztbackup/db /data/dbzt
- umount:
umount 10.30.31.8:/databk/ztbackup/db /data/dbzt
snmpd
/etc/default/snmpd snmpwalk -v2c -c public 10.30.43.10

